Motivation
New challenges, restrictions and degrees of freedom exist in the concept design of electrically driven vehicles. The specific components that influence the concept, such as electric energy storage, traction battery, etc., play an important role here.
- Electrical energy storage, traction battery
- Hydrogen storage
- Fuel cell system
- Electric drive system
- High-voltage electrical system
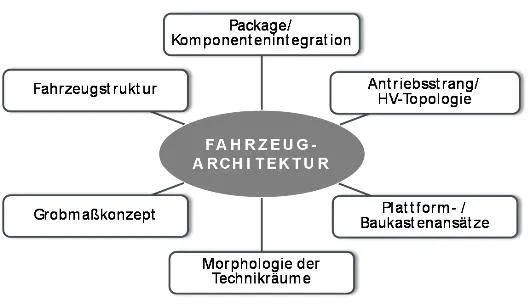
These core components harbour immense development dynamics with regard to their use in the vehicle, and their influence on the vehicle as a whole must be investigated. At the same time, the question arises of suitable vehicle architectures that allow the presentation of coherent overall concepts.
Goal
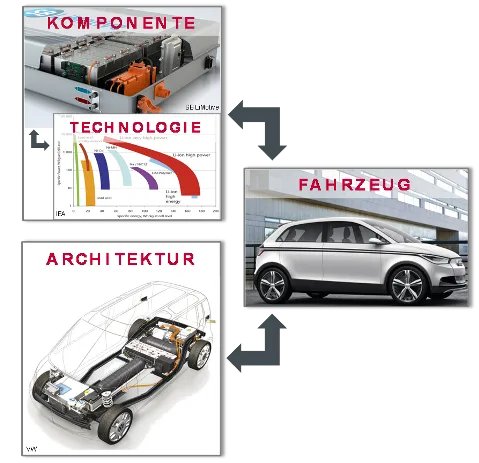
With regard to cross-series modular and platform strategies, the technical interactions between specific components, the vehicle architecture and the overall vehicle concept will be investigated. Based on the findings, implications for future electrified vehicle concepts will be developed: The use of technical potentials of components and technologies on the one hand and the appropriate design of the vehicle architecture on the other hand are essential.
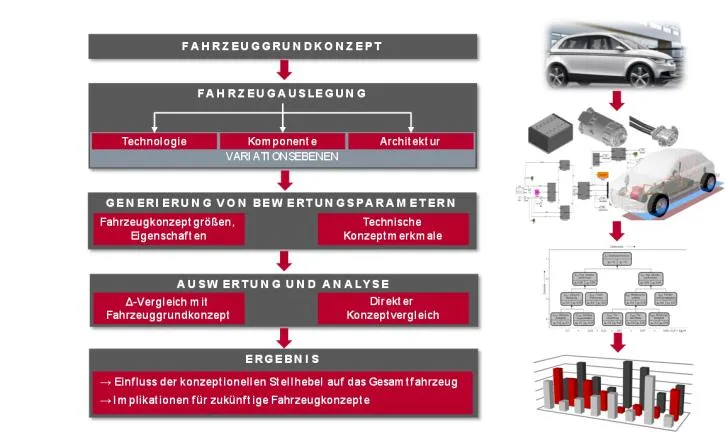
Implementation
The investigation of the functional and geometric interactions as well as the influences of concept-determining levers on the part of technology, components and vehicle architecture on the overall vehicle concept require suitable methodological support. A tool-supported design and analysis process is being developed for this purpose. Model-based tools for component design and overall vehicle simulation are coupled with a generic Digital Mock-Up (DMU). With the help of an integrated evaluation method, technical concept alternatives can be compared with regard to both classic vehicle characteristics and technical concept features. The implementation is based on MATLAB/Simulink, CATIA V5 and MS Excel.